Anxiety
Understanding Anxiety: Causes, Symptoms, and Coping Strategies
Understanding Anxiety: Causes, Symptoms, and Coping Strategies
Anxiety is a common emotional experience that can range from mild unease to intense fear or panic. It’s a natural response to stress, and in some situations, it can be beneficial, helping us stay alert and focused. However, when anxiety becomes overwhelming and persistent, it can interfere with daily life and lead to various mental health issues. With anxiety disorders affecting millions worldwide, understanding its intricacies is crucial for managing its impact on our lives. Anxiety disorders are a type of mental health condition. Anxiety treatment makes it easy to get through your day.
What is Anxiety?
Anxiety is a feeling of worry, nervousness, or unease about something with an uncertain outcome. It’s a normal response to stress or danger and can be helpful in some situations, such as before a job interview or during a test. However, for some people, anxiety can become excessive and difficult to control, leading to an anxiety disorder. Anxiety disorders are among the most common mental health conditions, affecting around 18% of adults in the United States each year.
Causes of Anxiety
Anxiety can be caused by a combination of factors, including:
1. Genetics: A family history of anxiety disorders can increase the risk of developing anxiety. Studies suggest that genetics can account for about 30-40% of an individual’s susceptibility to anxiety disorders.
2. Brain Chemistry: Imbalances in certain neurotransmitters, such as serotonin and dopamine, can contribute to anxiety. Neurotransmitters are chemicals that transmit signals in the brain, and an imbalance can affect mood regulation.
3. Environmental Factors: Stressful life events, such as the loss of a loved one, financial problems, or trauma, can trigger anxiety. Early childhood experiences, such as abuse or neglect, can also increase vulnerability to anxiety later in life.
4. Medical Conditions: Chronic illnesses, hormonal changes, and certain medications can cause anxiety symptoms. Conditions such as heart disease, diabetes, and asthma are often linked with higher anxiety levels.
5. Personality Traits: Certain personality types, such as perfectionists or those with low self-esteem, may be more prone to anxiety. Individuals who are more sensitive to stress or have a tendency to view the world as threatening may also experience higher levels of anxiety.
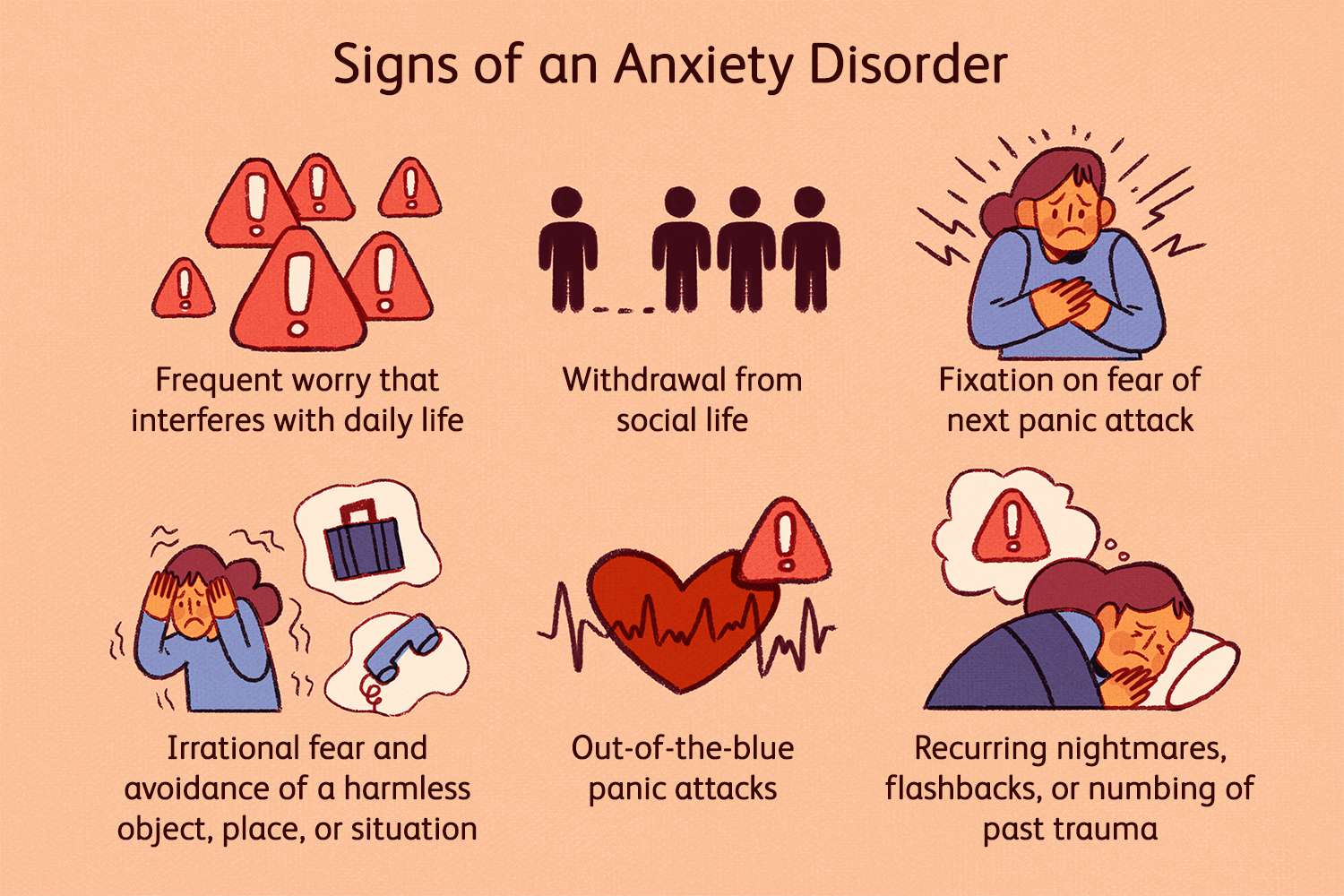
Symptoms of Anxiety
Anxiety manifests in various physical, emotional, and behavioral symptoms, which can vary from person to person. Common symptoms include:
1. Physical Symptoms:
- Increased heart rate
- Sweating
- Trembling or shaking
- Shortness of breath
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Gastrointestinal issues, such as nausea or diarrhea
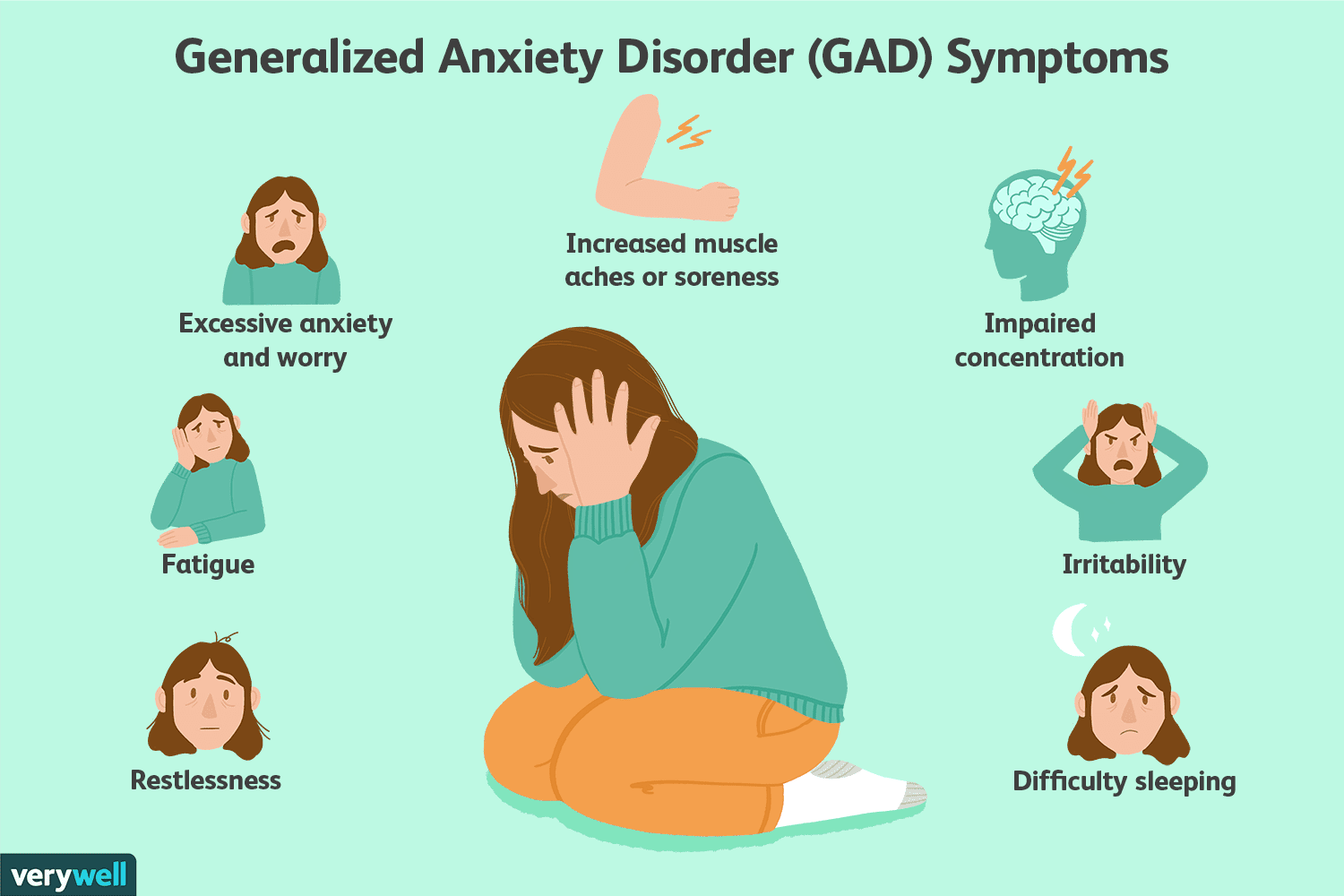
- Muscle tension
- Fatigue
2. Emotional Symptoms:
- Excessive worry or fear
- Restlessness or feeling on edge
- Irritability
- Difficulty concentrating
- Feeling overwhelmed
- Sense of impending doom
3. Behavioral Symptoms:
- Avoiding certain situations or places
- Difficulty sleeping or changes in sleep patterns
- Procrastination
- Seeking reassurance from others
- Changes in eating habits
- Increased use of alcohol or drugs to cope
Anxiety treatment makes it easy to get through your day. Some ways to manage anxiety disorders include learning about anxiety, mindfulness, relaxation techniques, correct breathing techniques, dietary adjustments, exercise, learning to be assertive, building self-esteem, cognitive therapy, exposure therapy, structured problem solving, medication and support groups.
Types of Anxiety Disorders
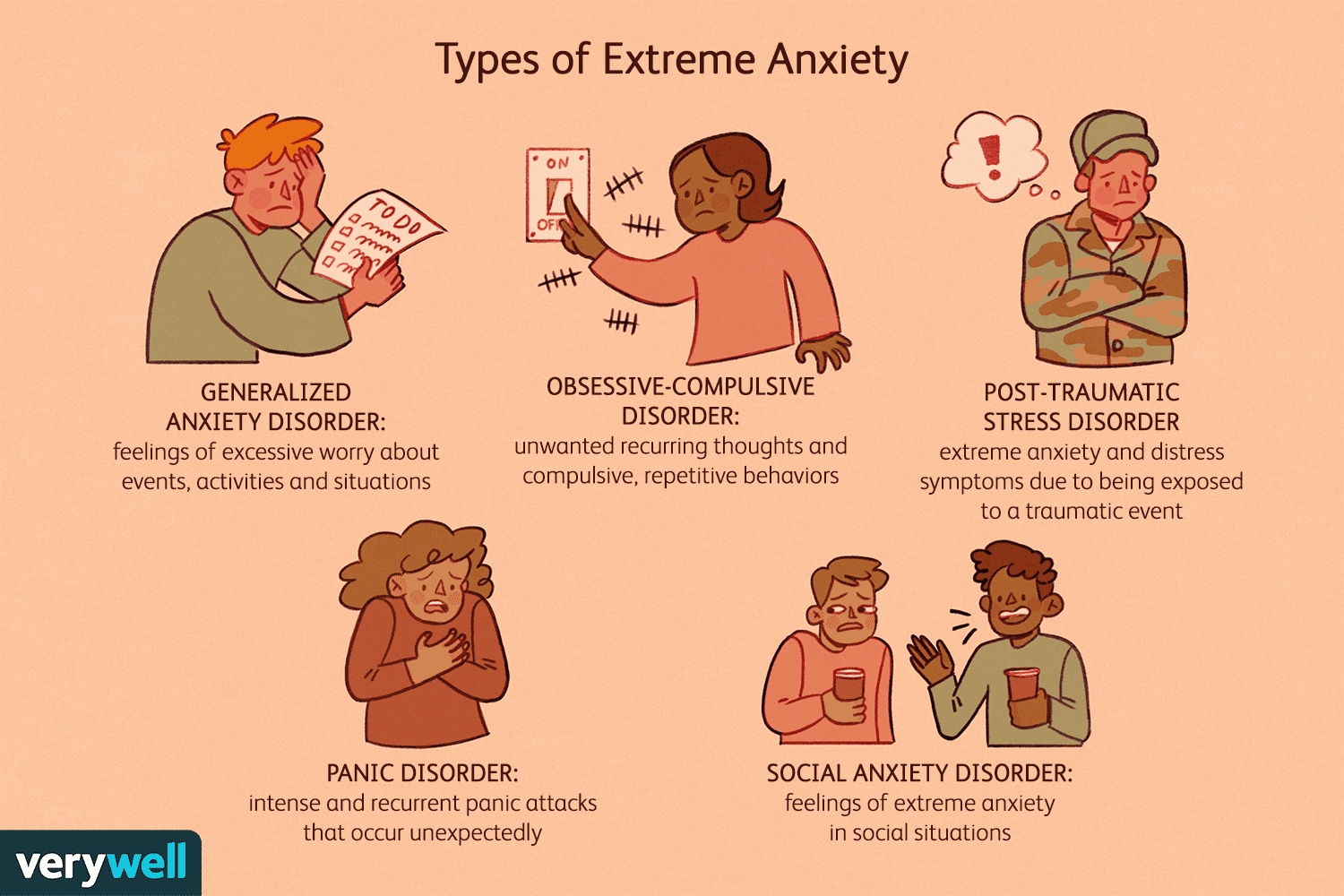
Anxiety disorders are a group of mental health conditions characterized by excessive and persistent anxiety. Some common types include:
1. Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD): Characterized by excessive, uncontrollable worry about various aspects of daily life. People with GAD often anticipate disaster and may be overly concerned about health, money, family, or work.
2. Panic Disorder: Involves recurrent panic attacks, which are sudden episodes of intense fear accompanied by physical symptoms. These attacks can occur unexpectedly and lead to persistent worry about future attacks.
3. Social Anxiety Disorder: Fear of social situations where one might be judged or embarrassed. This can lead to avoidance of social interactions and significant distress in daily activities.
4. Specific Phobias: Intense fear of specific objects or situations, such as heights, spiders, or flying. Exposure to the phobic stimulus can provoke immediate anxiety and panic.
5. Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD): Involves unwanted, repetitive thoughts (obsessions) and behaviors (compulsions) aimed at reducing anxiety. For example, excessive hand washing due to fear of germs.
6. Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD): Anxiety resulting from a traumatic event, characterized by flashbacks, nightmares, and severe anxiety. Individuals with PTSD may relive the trauma and experience heightened reactivity.
Coping Strategies on Anxiety Treatment
Managing anxiety involves a combination of self-help strategies, therapy, and sometimes medication. Here are some effective ways to cope with anxiety:
1. Lifestyle Changes:
Regular Exercise: Physical activity can reduce stress and improve mood. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise most days of the week.
Healthy Diet: Eating a balanced diet can support overall well-being. Foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, and complex carbohydrates can be particularly beneficial.
Adequate Sleep: Prioritize sleep to help manage stress and anxiety. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night. Establishing a regular sleep routine can help improve sleep quality.
2. Relaxation Techniques:
Deep Breathing Exercises: Practice deep breathing to activate the body’s relaxation response.
Progressive Muscle Relaxation: Tense and then relax different muscle groups to reduce physical tension.
Mindfulness Meditation: Focus on the present moment to reduce anxiety.
Yoga: Combines physical postures, breathing exercises, and meditation to promote relaxation.
3. Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT):
CBT is a highly effective therapy that helps individuals identify and challenge negative thought patterns and behaviors associated with anxiety. Techniques such as cognitive restructuring and exposure therapy are commonly used in CBT.
4. Anxiety treatment:
Antidepressants, anti-anxiety medications, and beta-blockers can be prescribed by a healthcare provider to help manage symptoms. Medications can be used short-term or long-term, depending on the individual’s needs.
5. Support Network:
Building a strong support network of friends, family, and support groups can provide emotional support and reduce feelings of isolation. Sharing experiences and talking about feelings can alleviate anxiety.
6. Professional Help:
Seeking help from a mental health professional, such as a psychologist, psychiatrist, or counselor, can provide specialized treatment and support. Therapies like CBT, dialectical behavior therapy (DBT), and exposure therapy are commonly used to treat anxiety disorders.
Conclusion
Anxiety is a common but manageable condition. By understanding its causes, recognizing its symptoms, and implementing effective coping strategies, individuals can take control of their anxiety and lead fulfilling lives. If anxiety becomes overwhelming, seeking professional help from a mental health provider is crucial. With the right support and treatment, it’s possible to overcome anxiety and improve overall mental health. Anxiety disorders are a type of mental health condition. Anxiety treatment makes it easy to get through your day.
Understanding anxiety and its impact on mental health is essential for promoting well-being and reducing the stigma associated with mental health disorders. Education, awareness, and compassion are key to supporting those affected by anxiety and fostering a society where mental health is prioritized and valued.
