Pain Relief
Pain Relief
Pain Relief
Physicians and other health professionals typically offer pain relief across various dimensions, addressing everything from acute and simple to chronic and challenging pain. Additionally, for more complex cases, they enlist support from a specialized medical field dedicated to pain management, known as pain medicine.
Accord Codeine Phosphate 30mg
Healthcare providers prescribe this medicine to adults for pain relief, cough relief, and symptomatic relief of prolonged loose stools (diarrhea). It’s also suitable for children over 12 years old who need short-term relief from moderate pain that isn’t alleviated by other painkillers like paracetamol or ibuprofen alone.

This medicine contains codeine phosphate, belonging to a class of medicines known as opioids, which effectively relieve pain.
Remember, your healthcare provider prescribed this medicine specifically for you and it should not be given to anyone else.
Additionally, opioids carry the risk of addiction, and stopping suddenly may result in withdrawal symptoms. Your prescriber should have explained the duration of treatment and when it’s appropriate to stop, as well as how to do so safely.
Furthermore, it can be used either alone or combined with other painkillers such as paracetamol.
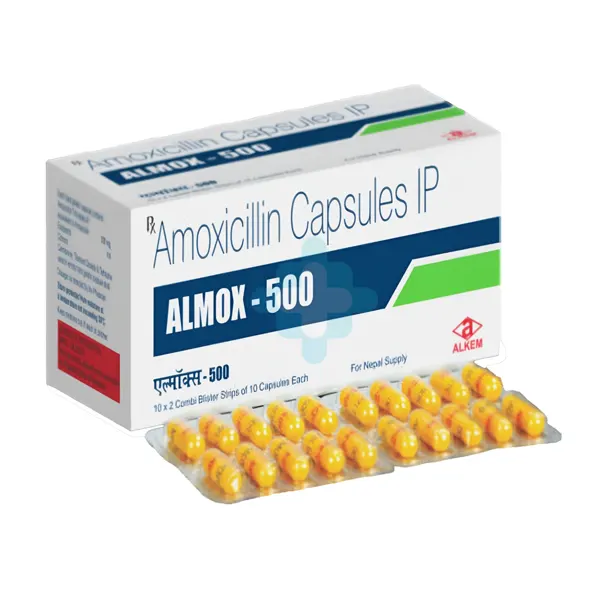
Amoxicillin Trihydrate IP 500mg
Amoxicillin, a penicillin antibiotic, effectively treats bacterial infections such as tonsillitis, bronchitis, sinusitis, pneumonia, and infections of the ear, nose, throat, skin, or urinary tract.
On the other hand, amoxicillin clavulanate combines amoxicillin with clavulanate potassium. While amoxicillin fights bacteria, clavulanate potassium helps prevent certain bacteria from developing resistance to amoxicillin.
Additionally, amoxicillin is sometimes paired with another antibiotic, clarithromycin (Biaxin), to address stomach ulcers caused by Helicobacter pylori infection. This treatment combination may also include a stomach acid reducer called lansoprazole (Prevacid).
Both 500 mg and 250 mg doses of amoxicillin are available in tablets or capsules, as well as in oral suspension. It’s important to note that numerous brands and formulations of amoxicillin exist, not all of which are listed in this leaflet.
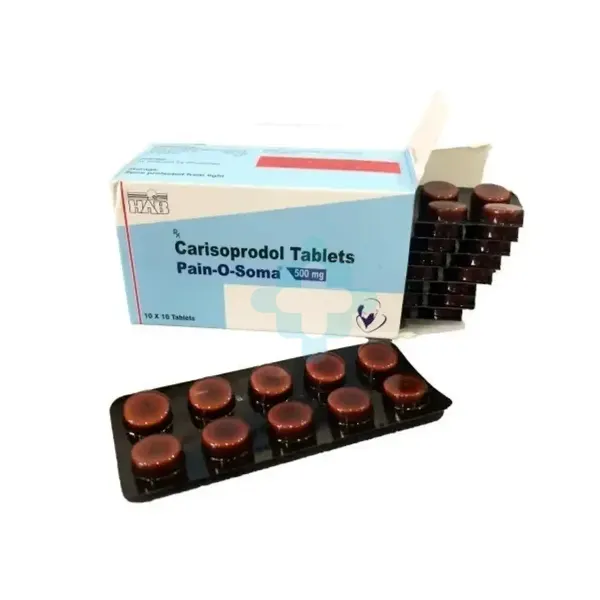
Carisoprodol 500mg
Carisoprodol 500 mg is a prescription muscle relaxant that relieves pain and discomfort from muscle injuries, spasms, and other musculoskeletal conditions.
Carisoprodol acts as a central nervous system depressant by interrupting neuronal communication within the reticular formation and spinal cord. This results in muscle relaxation and pain relief. The liver metabolizes it into meprobamate, which has sedative and anxiolytic effects.
Patients typically take 250 to 350 mg three times daily and at bedtime. For more severe symptoms, doctors may prescribe a 500 mg dose. The treatment usually lasts up to two or three weeks to avoid dependence, tolerance, and abuse.
Common side effects include drowsiness, dizziness, and headache. More serious side effects can include allergic reactions, seizures, and serotonin syndrome, especially when combined with other medications that increase serotonin.
Carisoprodol carries a risk of abuse and dependence, particularly with long-term use or higher doses. Stopping the medication suddenly after extended use can lead to withdrawal symptoms. People with acute intermittent porphyria or hypersensitivity to Carisoprodol or meprobamate should avoid this medication.
Using Carisoprodol with alcohol or other CNS depressants can enhance sedative effects and increase the risk of serious side effects. Additionally, it can interact with opioids, benzodiazepines, and certain antidepressants, leading to dangerous effects.
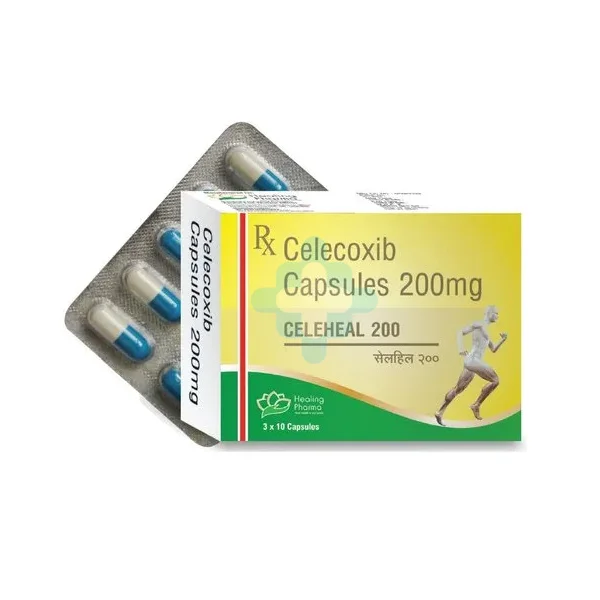
Celecoxib 200mg (Celeheal 200)
Celecoxib 200 mg, sold as Celeheal 200, belongs to the class of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and primarily relieves pain and inflammation. Doctors commonly prescribe it for arthritis, acute pain, and menstrual discomfort.
Celecoxib works by inhibiting the enzyme cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), which produces prostaglandins causing inflammation and pain. By selectively blocking COX-2, celecoxib reduces inflammation and alleviates pain while minimizing gastrointestinal side effects typically associated with non-selective NSAIDs.
Osteoarthritis: Reduces pain and inflammation.
Rheumatoid Arthritis: Manages symptoms.
Ankylosing Spondylitis: Treats pain and inflammation.
Acute Pain: Manages post-surgery or injury pain.
Primary Dysmenorrhea: Relieves menstrual pain.
Typical dosage for adults is 200 mg once daily or 100 mg twice daily, depending on the condition and patient’s response.
Side Effects
Common side effects include:
- Stomach pain
- Diarrhea
- Indigestion
- Gas
Serious side effects can include:
- Cardiovascular events (e.g., heart attack, stroke)
- Gastrointestinal bleeding
- Kidney issues
- Allergic reactions
Precautions
Cardiovascular Risk: Celecoxib may increase the risk of serious cardiovascular events, especially with long-term use or in individuals with existing cardiovascular disease.
Gastrointestinal Risk: Though less likely than non-selective NSAIDs, celecoxib can still cause gastrointestinal bleeding, ulcers, and perforation.
Kidney Function: It can affect kidney function, so monitoring is necessary, especially in patients with existing kidney issues.
Allergic Reactions: Those with allergies to sulfonamides should avoid celecoxib due to the risk of serious allergic reactions.
Other NSAIDs: Concurrent use with other NSAIDs can increase the risk of gastrointestinal bleeding.
Anticoagulants: Enhances the effects of blood thinners, increasing bleeding risk.
Antihypertensive Drugs: May reduce the effectiveness of certain blood pressure medications.
Codeine Phosphate & Sulfogatacol
Codeine phosphate and sulfogatacol combine in certain medications to provide both analgesic and expectorant properties.
- Codeine Phosphate:
- Type: Opiate (narcotic) analgesic.
- Uses: People use codeine phosphate primarily to relieve mild to moderate pain. Additionally, it acts as a cough suppressant in some cough medicines.
- Mechanism of Action: After ingestion, the body converts codeine into morphine. Morphine then binds to opioid receptors in the brain and spinal cord, altering the perception and response to pain. Moreover, it decreases activity in the part of the brain responsible for coughing.
- Sulfogatacol (also known as potassium guaiacolsulfonate):
- Type: Expectorant.
- Uses: This helps loosen mucus and phlegm in the airways, making it easier to cough up and expel.
- Mechanism of Action: It increases the production of respiratory tract fluid, which reduces the viscosity of mucus and facilitates its clearance from the respiratory tract.
When combined, these two components offer a dual-purpose solution in certain medications. Codeine phosphate alleviates pain and suppresses cough, while sulfogaiacol thins and loosens mucus in the lungs, making it easier to expel. Therefore, this combination effectively treats symptoms associated with respiratory conditions that require both pain relief and mucus clearance.
However, people should use such combination medications under the guidance of a healthcare provider due to the potential for side effects and the risk of dependency associated with codeine.
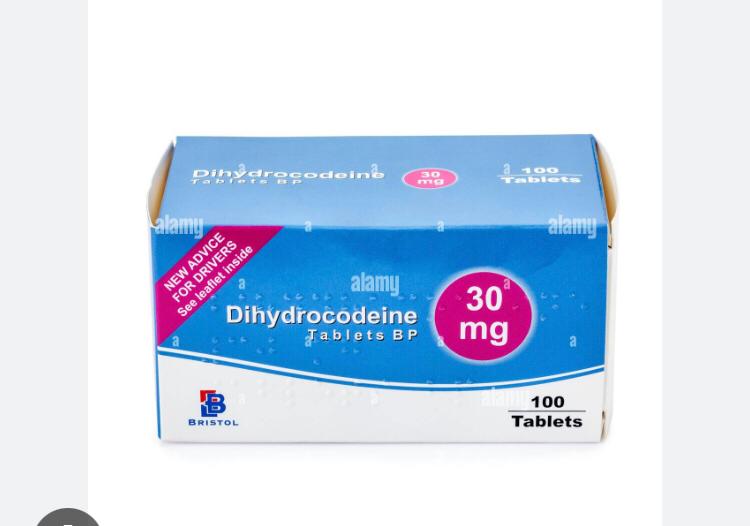
Dihydrocodeine 30mg Tablets
Dihydrocodeine 30mg tablets relieve moderate to severe pain and sometimes suppress coughing. This semi-synthetic opioid analgesic, similar to codeine, works effectively for many patients.
Pain Relief: People use dihydrocodeine to manage pain from conditions like arthritis, back pain, or post-surgical recovery.
Cough Suppressant: Occasionally, it helps suppress coughing.
Dihydrocodeine binds to opioid receptors in the brain and spinal cord, changing the perception of pain and suppressing the cough reflex.
Typical Dosage: Adults usually take 30mg every 4 to 6 hours, based on pain severity and response.
Administration: Take tablets orally, with or without food, following the doctor’s instructions to avoid side effects or dependence.

Side Effects
Common Side Effects: These include nausea, vomiting, constipation, drowsiness, and dizziness.
Serious Side Effects: These include respiratory depression, hypotension, severe allergic reactions, and potential dependency with long-term use.
Precautions
Dependency and Abuse: Use dihydrocodeine strictly as prescribed to avoid dependency and abuse risks.
Interactions: Avoid combining it with other central nervous system depressants like alcohol, benzodiazepines, and other opioids to reduce the risk of serious side effects.
Contraindications: Individuals with severe respiratory issues, acute asthma, or gastrointestinal obstruction should avoid using it.
Conclusion
In conclusion, pain relief medications like Accord Codeine Phosphate, Amoxicillin Trihydrate, Carisoprodol, Celecoxib, Codeine Phosphate & Sulfogaiacol, and Dihydrocodeine offer targeted solutions for various medical conditions. Their effective use requires careful adherence to prescribed guidelines, awareness of potential side effects, and ongoing communication with healthcare providers to ensure both safety and efficacy.
Pain relief medications offer diverse solutions tailored to specific needs, ranging from mild discomfort to severe pain and respiratory conditions. Each medication listed below serves distinct purposes and requires careful adherence to medical guidance to ensure efficacy and safety.
